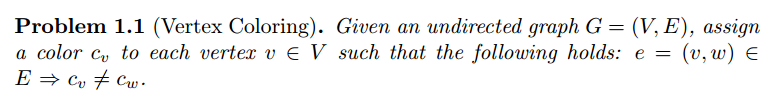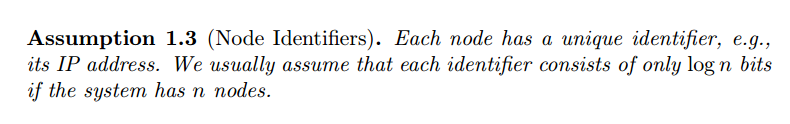Principles of Distributed System
分布式系统原理
要是能把这本书翻译了该多好呀,不多一周一节就行啊。希望如此下载链接
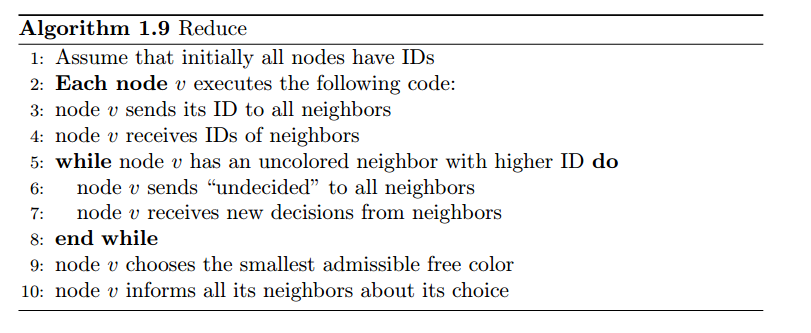
chapter1.vertext coloring(顶点涂色算法)
Vertex coloring is an infamous graph theory problem. It is also a useful toy
example to see the style of this course already in the first lecture. Vertex coloring
does have quite a few practical applications, for example in the area of wireless
networks where coloring is the foundation of so-called TDMA MAC protocols.
Generally speaking, vertex coloring is used as a means to break symmetries,
one of the main themes in distributed computing. In this chapter we will not
really talk about vertex coloring applications, but treat the problem abstractly.
At the end of the class you probably learned the fastest algorithm ever! Let us
start with some simple definitions and observations
顶点涂色算法提供了一些实用的小应用例如在以涂色为基础的无线网络领域中(TDMA MAC协议)。一般而言,做为一种打破均衡的手段,这也是分布式计算的一个重要主题之一。本
本节并不聊关于顶点涂色算法的应用,而是抽象的对待这个问题。从几个简单的定义来开始